Welcome fall in the price cap but high debt levels remain
- Publication type:
- Press release
- Publication date:
- Topic:
- Energy pricing rules
- Subtopic:
- Energy price cap
Energy regulator Ofgem has today (Friday 23 February, 2024) announced a significant reduction of the energy price cap for the second quarter of 2024.
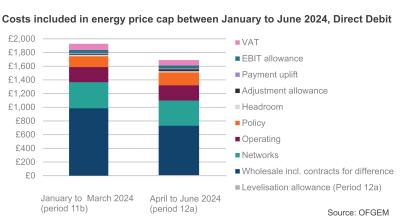
The price cap, which sets a maximum rate per unit that can be charged to customers for their energy use, will fall by 12.3% on the previous quarter from 1 April to 30 June 2024. For an average household paying by direct debit for dual fuel this equates to £1,690, a drop of £238 over the course of a year – saving around £20 a month.
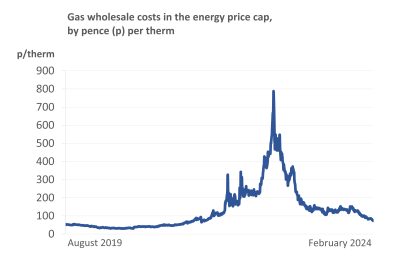
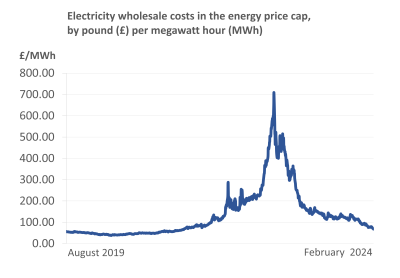
This will see energy prices reach their lowest level since Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine in February 2022 caused a further spike in an already turbulent wholesale energy market, driving up costs for suppliers and ultimately customers.
However, despite reaching this welcome milestone, Ofgem recognises that the cost of living remains high and many customers continue to struggle with their bills as standing charges rise and energy debt reaches a record figure of £3.1 billion.
Therefore, today Ofgem is also announcing:
- Confirmation of the levelisation of standing charges to remove the ‘PPM premium’ previously incurred by prepayment customers.
- A decision to allow a temporary adjustment to the price cap to address supplier costs related to increased levels of bad debt.
- A decision to extend the ban on acquisition-only tariffs (BAT) for up to another 12 months.
- Confirmation of the end of the Market Stabilisation Charge (MSC) from April 1.
- A decision not to change wholesale cost allowances following a review conducted in late 2023.
Jonathan Brearley, CEO of Ofgem, said:
“This is good news to see the price cap drop to its lowest level in more than two years – and to see energy bills for the average household drop by £690 since the peak of the crisis – but there are still big issues that we must tackle head-on to ensure we build a system that’s more resilient for the long term and fairer to customers.
“That’s why we are levelising standing charges to end the inequity of people with prepayment meters, many of whom are vulnerable and struggling, being charged more up-front for their energy than other customers.
“We also need to address the risk posed by stubbornly high levels of debt in the system, so we must introduce a temporary payment to help prevent an unsustainable situation leading to higher bills in the future. We'llbe stepping back to look at issues surrounding debt and affordability across market for struggling consumers, which we'll be announcing soon.
“These steps highlight the limitations of the current system – we can only move costs around – so we welcome news that the Government is opening the conversation on the future of price regulation, seeking views on how standard energy deals can be made more flexible so customers pay less if using electricity when prices are lower.
“But longer term we need to think about what more can be done for those who simply cannot afford to pay their energy bills even as prices fall. As we return to something closer to normality we have an opportunity to reset and reframe the energy market to make sure it’s ready to protect customers if prices rise again.”
Affordability remains the most significant issue, as people continue to struggle with bills over the last two years, which has led to record levels of energy debt.
To address this challenge in the short-term, Ofgem will allow a temporary additional payment of £28 per year (equivalent to £2.33 per month) to make sure suppliers have sufficient funds to support customers who are struggling. This will be added to the bills of customers who pay by direct debit or standard credit and is partly offset by the termination of an allowance worth £11 per year that covered debt costs related to the Covid pandemic.
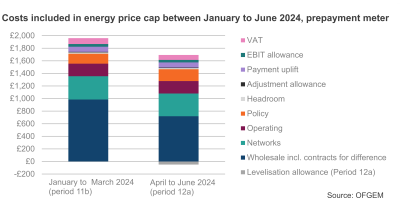
Prepayment meter (PPM) customers will not be impacted by the extra charge, reflecting the fact that many do not build up the same level of debt as credit customers because they top up as they go.
Ofgem also confirmed plans to maintain the equalisation of standing charges across payment methods so that customers are not charged more depending on the payment method they use. Since October 2022 the so-called ‘PPM premium’ was removed by government support via the Energy Price Guarantee. However, with that support coming to an end on April 1, Ofgem has taken steps to provide a lasting solution, which must be funded by bill payers rather than tax payers, to maintain fairness in the system.
This means PPM customers will save around £49 per year while direct debit customers will pay £10 per year more.
Increasing network costs has also contributed to the rise in standing charges – and in anticipation of this we published a call for input in November 2023 and are currently reviewing more than 40,000 responses.
Today Ofgem is also publishing a decision to extend the ban on acquisition-only tariffs (BAT) for another 12 months, but intends to open a consultation to consider shortening this extension to just six months.
The BAT was introduced in April 2022 to provide more stability at the height of the energy crisis, removing often risky short-term discounted tariffs intended to attract customers from other suppliers.
As competition returns to the market, Ofgem is encouraging rising numbers of customers switching with a number of measures, including shortening the time suppliers are given to complete a customer transfer from 15 days to just five.
Additionally, from 1 April, the Market Stabilisation Charge – introduced in tandem with the BAT – will come to an end, meaning suppliers are no longer required to compensate a new customer’s previous supplier when they switch.
This influenced the regulator’s decision to temporarily extend the BAT rather than remove both safeguards at the same time, ensuring a phased and responsible return towards normality in the market while preventing a return of the risky behaviours which contributed to the high number of supplier failures during the energy crisis.
Ofgem is also publishing a decision following its wholesale adjustment review. Following unusually high volatility in wholesale prices between October 2022 and September 2023, the regulator examined whether suppliers experienced differences between wholesale costs and the allowances they were allowed to recover via the price cap.
However, after careful consideration the regulator has concluded to take no further action as wholesale costs did not systematically differ from allowances.
Notes To Editors
The energy price cap was introduced by the government and has been in place since January 2019, and Ofgem is required to regularly review the level at which it is set. It ensures that an energy supplier can recoup its efficient costs while making sure customers do not pay a higher amount for their energy than they should. The price cap, as set out in law, does this by setting a maximum that suppliers can charge per unit of energy.
For prepayment customers the levelisation allowance is -£49 excluding VAT, -£52 including VAT.
Updated number of customers on different tariff types as of January* 2024
New no. of customers on SVTs – ‘around 29 million’
New no. of SVT (non-PPM) customers – ‘around 24 million’
New no. of SVT PPM customers – ‘around 4 million’
Total number of customers on fixed tariffs: 'around 3 million' (with the vast majority being non-PPM)
*Latest Financial Responsibility RFI data is for January 2024. Tariff and Customer Account RFI data is for January 2024 (used to calculate the SVT payment method splits)